low end tidal co2 during cpr
These levels of CO 2 were consistent with effective chest compression. Arterial diastolic pressure 25 mm Hg may be useful but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line.

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
A low P a CO2 level is correlated with increased risk of cerebral edema in.

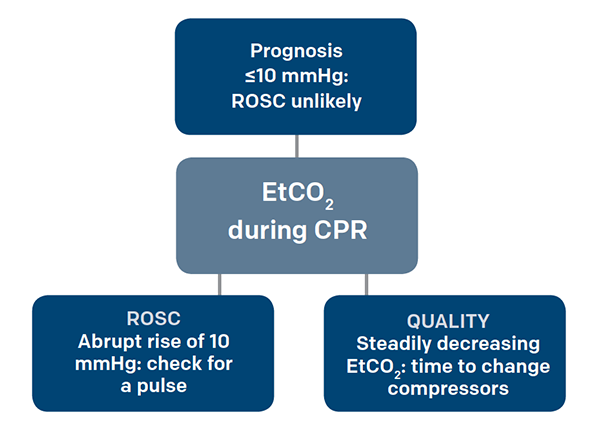
. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. Systematic review and meta-analysis of end-tidal carbon dioxide values associated with return of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The height of the capnography waveform accompanies this number on the.
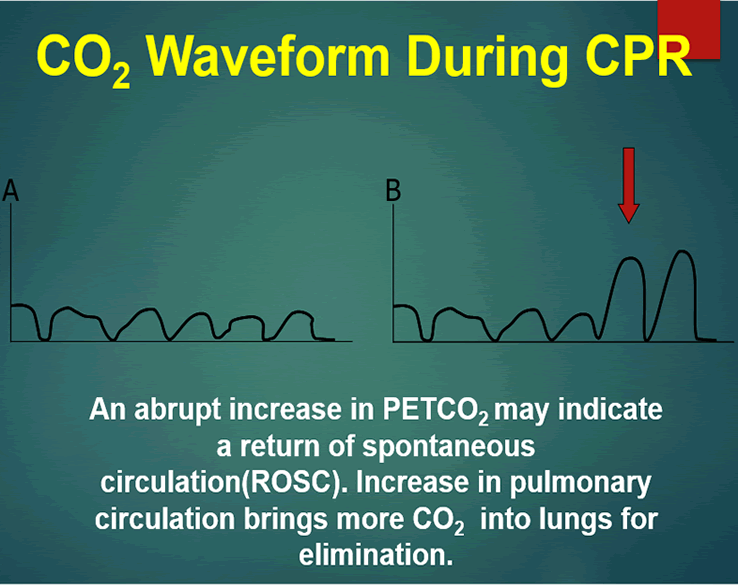
This pattern not previously described is different from that observed in animal and adult cardiac arrest caused by ventricular fibrillation during which ETCO2 decreases to almost zero after the onset of arrest begins to increase after the onset of effective CPR and increases to. The first sign of the return of spontaneous circulation ROSC during CPR is increase in ETCO2. 4 to 5 CO2 PetCO2 vs.
Teams should aim for EtCO2 at least 10 mm Hg and ideally 20 mm Hg. Uses during cardiac arrest. During CPR with manual ventilation end-tidal CO2 is generally.
Multiple monitoring options so you can choose what and how to monitor respiratory status. Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. End-tidal CO2 is defined as the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in exhaled air at the end of expiration.
Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going. Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC. This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement.
Low end tidal co2 during cpr. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient. The end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 is defined as a partial pressure of carbon dioxide at the end of an exhaled breath.
During CPR ETCO2 levels were initially high decreased to low levels and increased again at ROSC. During CPR ETCO2 levels were initially high decreased to low levels and increased again at. We typically assess quality of CPR by palpable pulses but this can be challenging and even unreliable.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 correlates with systemic blood flow and resuscitation rate during cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR and may potentially direct chest. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. Ensure proper rate approximately.
Throughout the resuscitation end-tidal CO 2 was consistently in the 28-36 mmHg range during VFCPR. Where do these numbers come from. EtCO2 is essentially to ensuring quality CPR.
More Than Just a Number. Evidence suggests a persistently low. And it has been found to correlate with.
Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed. Goal is 10 mmHg during CPR. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
These values are approximately 14. Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest. What should end-tidal CO2 be during CPR.
Ad View a brochure to learn about end-tidal CO2 capnography. Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists. Thus ETco 2 monitoring is a noninvasive way to measure coronary artery blood flow and return of spontaneous circulation during CPR.
Capnography may be especially useful in cardiac arrest patients as other conventional markers of endotracheal tube placement may be less reliable in these patients. However EtCO2 provides the same information an.

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

4 Things Paramedics Need To Know About Capnography And Heart Failure Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Cpr Mobile Code Stand With Capnograph Capnography
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project